The explosive growth of humanoid robots represents a prominent transformation in China’s innovation landscape during 2024.
As an influx of capital stimulates the emerging sector, human-like machines are being honed to superior agility and their versatile applications are becoming increasingly evident in a range of scenarios.
“Humanoid robots have now reached the educational level of a middle or high school student, and are expected to take the college entrance exam next year, which portends their deployment in more scenarios,” commented Hu Debo, general manager of Shanghai-based Kepler Robot.
NEW CAPABILITIES
In March, Hangzhou-based Unitree Robotics released a video showing its 50-kilogram Unitree H1 humanoid robot as it performed a standing somersault, a first for a full-scale electric humanoid.
Two months later, a robot developed by Beijing’s RobotEra ascended the Great Wall, showing its stability and strength on different types of terrain. A Beijing-based startup firm’s new STAR1 model also completed a long-distance run in the Gobi Desert in October, where it reached a speed of six meters per second.
Shenzhen-based Engine AI unveiled the robot with the most human-like gait and the promotional video immediately went viral.
The evolution of these robots has captured public attention on social media platforms and has also secured venture capital to fuel their growth.
From January to October 2024, at least 69 humanoid robot funding events took place globally, raising more than 11 billion yuan ($1.51 billion). Of those events, 56 took place in China and raised more than 5 billion yuan, according to partial data from GGII, a Shenzhen-based consulting firm for emerging industries.
The size of the humanoid robot market in China in 2024 is about 2.76 billion yuan, a recently published blue book showed.
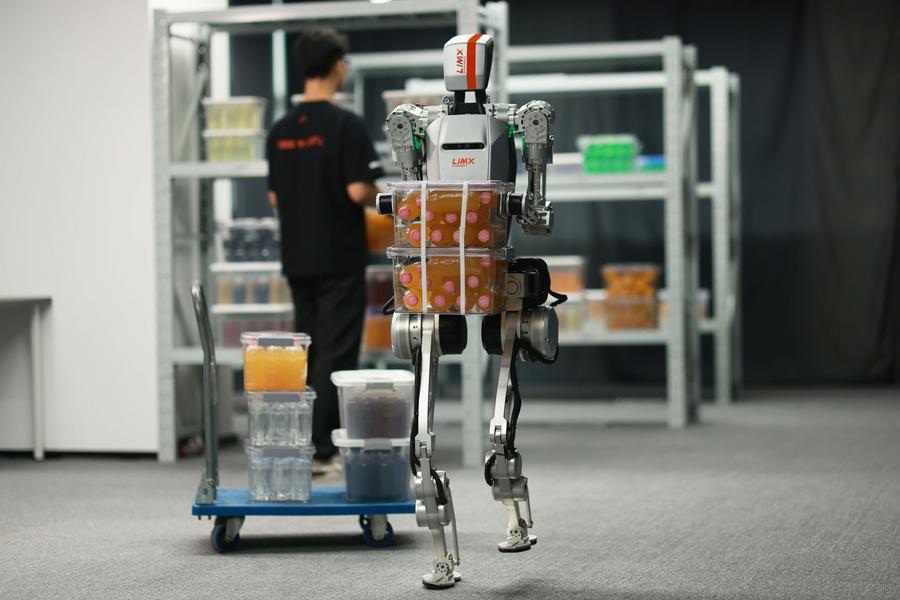 (241213) – SHENZHEN, Dec. 13, 2024 (Xinhua) – Undated file image of a CL-1 humanoid robot performing heavy cargo delivery tasks at a science and technology company, in Shenzhen, South China’s Guangdong province. The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, with its outstanding R&D capabilities and strong manufacturing base, serves as fertile ground for the development of the humanoid robot sector. In recent years, various vertical areas in the humanoid robot sector, ranging from basic components to system integration, have been flourishing in the Greater Bay Area. Numerous technology companies and research institutions have proliferated here, infusing greater intelligence and dexterity into humanoid robot products, which are gradually being implemented in the fields of industrial operation, medical care, education and research, and others. (Xinhua) (jg) (da) (vf)
(241213) – SHENZHEN, Dec. 13, 2024 (Xinhua) – Undated file image of a CL-1 humanoid robot performing heavy cargo delivery tasks at a science and technology company, in Shenzhen, South China’s Guangdong province. The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, with its outstanding R&D capabilities and strong manufacturing base, serves as fertile ground for the development of the humanoid robot sector. In recent years, various vertical areas in the humanoid robot sector, ranging from basic components to system integration, have been flourishing in the Greater Bay Area. Numerous technology companies and research institutions have proliferated here, infusing greater intelligence and dexterity into humanoid robot products, which are gradually being implemented in the fields of industrial operation, medical care, education and research, and others. (Xinhua) (jg) (da) (vf)
DRIVEN BY ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Currently, artificial intelligence (AI) has served as the “engine” incentivizing this advancement.
“The deep integration of humanoid robots with AI is a significant trend in the robotics industry this year,” said
Yang Fengyu, founder and CEO of UniX AI, a robotics technology firm in Shanghai.
“In the past, robots lacked autonomous motion control capabilities and could only perform individual tasks in a fixed environment, having difficulty adapting when the environment changed,” Xiong Youjun, general manager of the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center, told Xinhua.
The advancement of large-scale AI models not only makes robots smarter but also significantly reduces their production costs.
China has an extensive supply chain and manufacturing infrastructure, enjoys good policy support and vast market potential, and also has a large pool of technical talent, Xiong added.
APPLICATIONS
This month, a Chinese technology firm announced the start of large-scale production of multipurpose robots. AgiBot, a startup established in February 2023, already produced about 1,000 units of these humanoid robots.
Automotive production lines are among the most rapidly deployed scenarios for humanoid robots. UBTECH Robotics, a major robotics firm based in Shenzhen, has integrated its products into the training programs of automakers such as BYD, NIO and Geely.
Xpeng, another new energy vehicle manufacturer, has dabbled in robotics directly and the robots it has developed on its own are being trained in manufacturing scenarios.
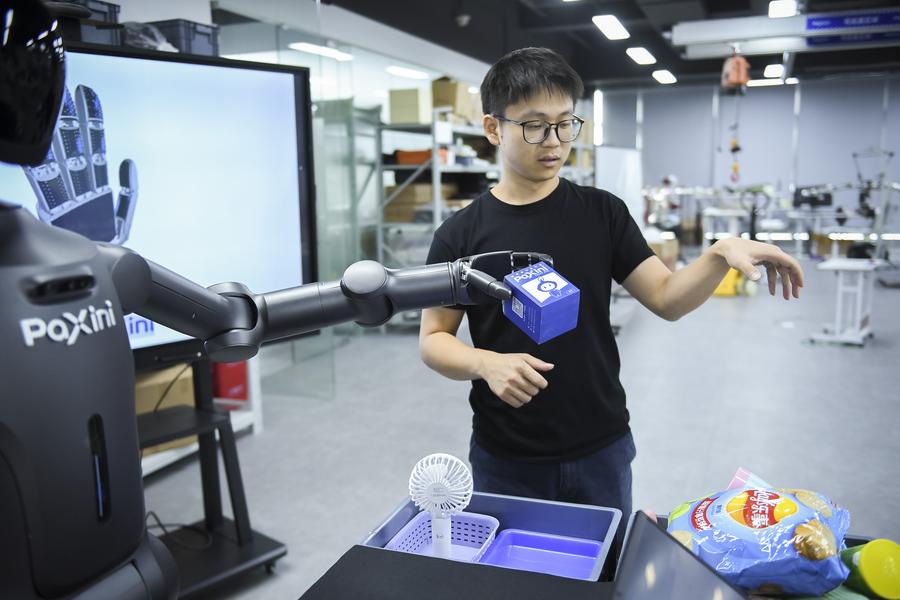
(241213) – SHENZHEN, Dec. 13, 2024 (Xinhua) – June 28, 2024 image of an employee testing the gripping ability of a TORA-ONE humanoid robot at a science and technology company, in Shenzhen, South China’s Guangdong province. The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, with its outstanding R&D capabilities and solid manufacturing base, serves as fertile ground for the development of the humanoid robot sector. In recent years, various vertical areas in the humanoid robot sector, ranging from basic components to system integration, have flourished in the Greater Bay Area. Numerous technology companies and research institutions have proliferated here, infusing greater intelligence and dexterity into humanoid robot products, which are gradually being implemented in the fields of industrial operation, medical care, education and research, and others. (Xinhua/Mao Siqian) (jg) (da) (vf)
The development of humanoid robots for home care services has begun to take shape, although implementation is slower than in industrial settings.
In September, Tencent’s Robotics X Lab unveiled “The Five,” a hybrid home care robot that has four wheels, tactile skin and hands. Images from lab tests show that the residential robot is capable of walking, carrying objects and helping seated elderly people stand up in a nursing home in Shenzhen.
“The Five” is still in prototype stage and needs further technological improvements before it can be effectively deployed in nursing homes, Robotics X said.
China’s booming humanoid robot market still faces several challenges. Rapid growth is hampered by “reliance on foreign high-end chips and proprietary algorithms, plus a shortage in domestic computational resources,” Xiong noted.
